Different types of primates
Taxonomic charts of the dwelling primates could be discovered under. The primates are divided into two main taxonomic teams: strepsirrhines, which retain primitive traits, such because the lemurs of Madagascar and the bushbabies of Africa, and the more derived haplorrhines, that’s, the tarsier, monkeys, and apes. The older phrases for the suborders which might be nonetheless in standard use are Prosimii and Anthropoidea.
However, tarsiers (small, nocturnal prosimian from the islands of the Southeast Asian archipelago) have traits of each team. The strepsirrhine primates have more typical mammalian noses or rhinaria which might be moist and more advanced with different types of primates.
They have a bigger olfactory bulb within the frontal cortex of their brains and scent glands in varied areas of their bodies. They use these glands to speak to different members of their species. We haplorhines have less complicated, dry noses and don’t odor nearly as good!
Primates are thought of as generalist mammals. Different types of primates have a skeletal construction that enables a large range of movement of the limbs. This is mirrored within the variety of ways in which they transfer round.
They could leap, climb, brachiate (swing from branch to branch), stroll on all 4 legs, or stroll on two legs. Their comparatively unspecialized extremities with long digits and nails (as an alternative of claws) are able to many various features — not like, for instance, the more specialized clawed feet of cats or canines.
Primate Classification and Phylogeny
Primates are a really various order. There are more than 50 primate genera and a whole bunch of various species of different types of primates. New primate species are nonetheless being found. Dozens of the latest species of primates have been found because of the year 2000 alone!

Prosimians and Anthropoids
The conventional classification of primates doesn’t essentially mirror their evolutionary history. It is predicated primarily on morphological similarities, quite than widespread ancestors.
However, a number of the conventional taxa are nonetheless generally used, so you will need to be accustomed to different types of primates. Primates have historically been divided into two main teams, referred to as prosimians and anthropoids (or simians).
Prosimians embody lemurs (just like the one pictured above), lorises, and tarsiers. Anthropoids embody monkeys, apes, and people.
Prosimians are typically small in size and have traits much like the earliest primates, whereas anthropoids are typically bigger and fewer much like early primates.

Phylogeny
Today, different types of primates are typically categorized on the idea of their evolutionary history. This kind of classification is predicated on a branch of science referred to as phylogeny. It exhibits how species are associated with widespread ancestors.
The tree under exhibits the phylogeny of primates. For comparability, the normal classification of primates into prosimians and anthropoids is included on the top of the phylogenetic tree.
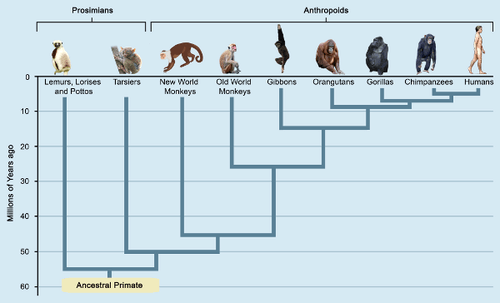
Do you discover a discrepancy between the phylogeny of different types of primates within the tree diagram and the normal, morphological classification? Tarsiers historically have been grouped with the prosimian lemurs and lorises, however, they’re now positioned in a separate group. This is as a result of tarsiers shared a more current widespread ancestor with anthropoids than did the opposite prosimians.
The phylogenetic classification additionally exhibits how New World monkeys branched off from Old World primates before the latter diverged into Old World monkeys and apes.
The phrase apes is a normal time period that refers to modern gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and people, in addition to their ancestors following the break up from Old World monkeys. Based on the phylogenetic tree, who are our closest dwelling family members? With which group did we share the newest widespread ancestor?

Major Events in Primate Evolution
If you have a look at the left facet of the phylogenetic tree above, you possibly can see roughly how long ago the totally different teams of primates diverged from their widespread ancestors.
As we are taught more about biochemical and evolutionary relationships among the many varied teams of primates, primate taxonomy is altering. The New World monkeys have modified considerably lately, with the creation of a number of households that have been previously grouped into two or three.
The Old World anthropoids (monkeys and apes) and New World monkeys are additionally distinguished by our noses. Old World anthropoids have more ovoid, downward-facing nostrils, whereas New World monkeys’ nostrils are round and forward-facing.
The Old World monkeys are divided into the cercopithecines, with their cheek pouches and more generalized diet, and the leaf-eating colobines, with their advanced guts. Think baboon (Africa) or snow monkey (Japan) for the previous and black-and-white colobus (Africa) or Hanuman langur (primarily Indian subcontinent) for the latter.

Earliest Primates
Based on fossil and molecular proof, the first primates could have developed as early as 55 to 65 million years ago. An early shut primate relative — the genus named Plesiadapis — left plentiful fossil stays in North America and Europe that date to 55-58 million years ago, however could have originated earlier.
Plesiadapis was a small, a minimum of partly arboreal mammal that will have eaten fruits and leaves. This now-extinct genus had a small mind and claws as an alternative to nails.
Its eyes have been situated on the perimeters of the pinnacle, which meant it lacked stereoscopic (three-dimensional) vision. With these traits, Plesiadapis itself was not a primate, but it surely was a possible ancestor of primates.
Divergence Within the Primates
Once the first primates emerged, different types of primates continued to evolve till the present. During that long time span, primates underwent a collection of evolutionary divergences, through which the main teams of primates branched off and new widespread ancestors emerged.
The first main divergence in all probability occurred near 60 million years ago when the lineage that will evolve into modern lemurs and lorises branched off from different early primates.
The divergence that led to the tarsiers in all probability dates to about 55 million years ago. The earliest tarsier-like fossils are discovered at the moment in East Asia.
The emergence of the widespread ancestor of all anthropoid primates (modern monkeys, apes, and humans) is assumed to have occurred around 40 million years ago, probably in Asia, as properly. If the earliest anthropoids did evolve in Asia, they quickly dispersed throughout Asia into Africa.
The group of anthropoids that will evolve into modern New World monkeys in all probability break up from their African ancestors a minimum of 35 million years ago.
different types of primates traveled from Africa to South America throughout the Atlantic Ocean, which was a lot narrower then. Most probably, a couple of primates have been carried out to sea on a natural raft of vegetation, and have been then carried to the New World by currents.
A possible widespread ancestor of Old World monkeys, apes, and people was the genus Aegyptopithecus, which lived around 35-33 million years ago. It was about 56 to 92 cm (22 to 36 in) in size and weighed about 6.7 kilograms (17.7 lb). Aegyptopithecus lived in subtropical forests, the place it was most certainly an arboreal quadruped that consumed fruit.
The Old World monkeys had diverged from the group that right now contains simply apes and people by 23 million years ago. A possible widespread ancestor of each ape and people is the species Proconsul africanus, which lived about 23 to 14 million years ago. It was in all probability an arboreal quadruped, which means that it walked on 4 limbs and fed primarily on fruit. It had a mind bigger than a modern monkey, however not as giant as a modern ape.
Ancestors of gorillas diverged from the apes that will finally evolve into chimpanzees and people about eight million years ago in Africa. Approximately six million years ago in Africa, the chimpanzee and human lineages lastly diverged.
The first true human ancestors developed not long after that. You can examine this era of primate evolution intimately within the idea of the Evolution of the Human Family.
Primate Evolutionary Trends
The important evolutionary pattern of different types of primates has been the elaboration of the mind. Comparative research presents a continuing pattern towards higher intelligence going from prosimians to New World monkeys to Old World monkeys to apes and at last to people.
The part of the mind that has elevated probably the most is the neocortex, which is the part of the mind concerned with the sensory notion, generation of motor instructions, spatial reasoning, and aware thought.
In human primates, the neocortex can also be concerned with language. While different mammals rely closely on their sense of odor, the arboreal lifetime of primates has led to a tactile (contact) and visually dominant sensory system. At the identical time, there was a discount within the olfactory (smell-related) elements of the mind.
With their giant brains, primates have superior cognitive skills. One indication of that is their tool use. Besides people, many different species of primates, particularly anthropoids, have been noticed utilizing gadgets of their atmosphere as instruments. The gorilla pictured under is utilizing a stick to check the depth of water as she wades by it.
Monkeys have been documented cracking nuts by inserting them on an “anvil” stone and hitting them with one other giant stone. Monkeys additionally use stones to crack open crabs and different shellfish. Some primates make instruments, as properly.
Chimpanzees, for instance, strip leaves from twigs and insert the twigs into termite mounds to “fish” for edible bugs. They additionally sharpen sticks to make use of as spears for searching small mammals.
Another pattern in primate evolution has been a growing dependence on advanced social behavior. Primates are among the many most social of animals. They reside in mated pairs, small family teams, or teams of as much as dozens of people.
Cooperation throughout the group helps to make sure that all group members survive. Cooperative social behaviors embody grooming, meal sharing, and collective protection in opposition to predators or of territory.
Now the International Union for Conservation of Nature acknowledges properly over 600 primate species and subspecies… and counting.
This organization additionally periodically highlights the imperiled standing of the top 25 threatened primate species, although the unhappy reality is that there are numerous more species that might simply qualify for these “top” slots.
Other Recommended Reading
- Orange Monkeys are the Rarest in the World?
- What is the Average Size of a Silverback Gorilla?
- How Much Does a Gorilla Weigh?
- Facts, Features, and Types of Gorillas
- Big Nosed Monkey (Nasalis larvatus) Facts and Profile
- Spider Monkey – What is Special about a Spider Monkey?
- Vervet Monkey Description, Habitat, and Facts
- How Long do Gorillas Live in the Jungle and In Captivity?
- Strongest Gorilla – Is a Gorilla Stronger than a Lion?
- Proboscis Monkey Facts and Information
- Different Types of Monkeys around the World
- Mandrillus Drills Description and Facts
- Chimpanzee Locomotion – Are Chimpanzees bipeds?
- Pygmy Slow Loris Facts – Untold and Interesting
- Bornean Slow Loris (Nycticebus borneanus) Facts
- Pygmy Slow Loris Facts | Baby | Venom | Habitat
- Slow Loris Facts, Information, and Conservation Status
- Bengal Slow Loris Facts and Information
- Madame Berthe’s Mouse Lemur Facts
- Northern Sportive Lemur Description and Traits
According to 2012 put up by the IUCN, “More than half (54%) of the world’s 633 primate species and subspecies with known conservation status are classified as threatened with extinction on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.”
Just a few new purported primate species are found each year. The most not too long ago described species is a Tibetan monkey, the white-cheeked macaque (Macaca leucogenys). However, we can’t really say that we have now found some 4 hundred never-before-seen sorts of primates prior to now few a long time.
Most probably, the obvious explosion in various kinds of primates is because of the more and more deep data of our planet’s biodiversity.
At the macroscopic level, we’re exploring the final uncharted locations on earth, utilizing more subtle monitoring and different gear that allow us to describe the natural world in an unprecedented element.
Two teams of monkeys that look identical by foggy binoculars could have documented bodily variations when noticed shut up through camera traps.
And on the microscopic level, our understanding of genetic variations has elevated dramatically, too.
On occasion, we have now long identified that people have 46 chromosomes, however solely not too long ago have we discovered that the 4 important sorts of gibbons (Nomascus, Hylobates, Hoolock, and Symphalangus) have wherever from 38 to 52 chromosomes!
Two populations of gibbons that look fairly comparable sitting high within the timber could end up having constant genetic variations as soon as the sequences are run. Learn more about different types of monkeys.
